Web V1
Points N/A
Solves N/A
This is my first time making a website using Python!!!! :D http://103.163.139.198:12312
by daffainfo
In this challenge, we have access to a web application that allows login and registration. Since the source code was provided, we can start by analyzing it to understand the vulnerabilities.
Vulnerability Discovery
The key vulnerability here lies in how the /internal endpoint is protected. According to the code, it restricts access to the IP address 127.0.0.1 (localhost), meaning only requests coming from the server itself can access this endpoint:
@app.route('/internal')
def internal():
if request.remote_addr != '127.0.0.1':
abort(403)
return "Flag: IFEST13{fake_flag}"However, there is another endpoint, /admin/fetch, which is intended to be used by admins. This endpoint allows users to input a URL, and the server fetches the contents of that URL. If the URL contains daffainfo.com, it will be fetched successfully.
@app.route('/admin/fetch', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def admin_fetch():
if 'user_id' not in session:
return redirect('/login')
user = db.session.get(User, session['user_id'])
if user.is_admin != '1':
return "You are not authorized.", 403
result = None
if request.method == 'POST':
url = request.form.get('url')
if 'daffainfo.com' not in url:
result = "Error: Only URLs with hostname 'daffainfo.com' are allowed."
else:
try:
resp = requests.get(url, timeout=5)
result = resp.text
except Exception as e:
result = f"Error fetching URL: {str(e)}"We notice that daffainfo.com is hardcoded as the allowed domain, and the URL entered by the user must contain this string. However, the check is not strict enough, as it allows us to input http://127.0.0.1:1337/internal?daffainfo.com, which will bypass the restriction and access the /internal endpoint.
Registering as Admin
Another vulnerability is that the registration endpoint allows user data to be inserted directly into the database:
@app.route('/register', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def register():
if request.method == 'POST':
data = request.form.to_dict()
data['password'] = hash_password(data['password'])
user = User(**data)
db.session.add(user)
db.session.commit()
return redirect('/login')
return render_template('register.html')In this case, there is no validation or restriction on setting the is_admin field when a user registers. By manipulating the registration form, we can set is_admin = 1 for our user, which gives us admin privileges. Once we register as an admin and log in, we gain access to the /admin/fetch endpoint and can retrieve the flag using the previously crafted URL.
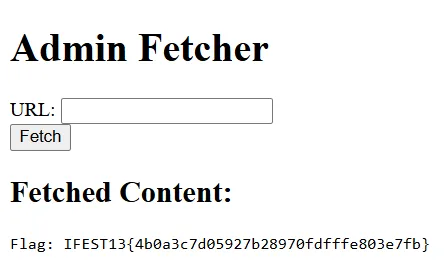
IFEST13{4b0a3c7d05927b28970fdfffe803e7fb}